Everything’s Changing: Cannabis
We are at the threshold of the future of medicine: The side effects of the previous generation’s pharmaceutical abuse has surfaced among the modern world illuminating the misleading nature of large pharmaceutical companies, incomplete studies, and falsified data all in the quest for higher profit margins. Now taking our first steps of the 21st century, patients and physicians alike can gather information about clinical research, active ingredient science, prescription bioavailability, and negative side effects — allowing the age of information to strengthen every individual in their personal healthcare and their growth in our ever-changing ecosystem.

Hemp vs. Marijuana
Cannabis has a variety of different flowering plants in it’s family, but the two focused on by medical professionals are Hemp and Marijuana. Marijuana’s name is distinct; you’ve probably heard about it since you were in middle school, maybe you have tried it, know someone who has tried it, or have eaten mysterious brownies prepared by your Aunt that made you feel ‘funny.’ Marijuana is the mainstream cannabis product commercialized for medical use, recreational use, and ‘drug war’ / ‘immoral failure’ propaganda in the U.S. It has many healing properties, but side effects that a majority of consumers find to be off-putting; even in this sense, the commercial tag line used by ‘burn outs’ for decades is “It’s good for you / it fights cancer/ you’ll be super healthy,” and where that is true (in a sense), it was mainly a tactic to try and pressure you into partaking in highly mutated, artificially enhanced ‘skunk’ weed.
Just like pharmaceuticals have been carefully designed and formulated for specific causes in the body, so has cannabis for medicinal use. Hemp, traditionally used for textiles, also carries many healing properties through it’s structure. Hemp contains high amounts of CBD from leaf to steam, however does not have the same ease of consumption as Marijuana (Remember this, it will be important later). Marijuana, high in THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol), has been reported to help patients relieve pain, nausea, and reduce inflammation; CBD (cannabidiol), found in trace amounts in Marijuana, can help in the treatment of seizures, reducing the effects of anxiety and paranoia, and even counteract the psychoactive effects of THC. Upon further investigation into these side effects and treatments, it was determined that THC is a thousand times more potent than CBD — meaning that a patient, to feel ‘high,’ would have to smoke 1,000 joints of genetically modified CBD cannabis. (Remember this, it will be important later).

Are Hemp and Marijuana The Same?
No. Hemp is completely different from marijuana in its function, cultivation and application. Marijuana, as it is widely known, is used for medicinal or recreational purposes. Hemp is used in a variety of other applications that marijuana couldn’t possibly be used in. These include healthy dietary supplements, skin products, clothing and accessories. Marijuana contains many chemical compounds that create the different characteristics of the plant — but the most important chemicals in marijuana are the cannabinoids.
What Exactly Is CBD and How Does It Work?
Cannabidiol (CBD), harvested through the leaves, resin, and flowers of Hemp or Marijuana is an active, non-psychoactive ingredient used in the treatment of various internal and external conditions of the body. CBD is one of over 60+ naturally occurring cannabinoid compounds found in Cannabis.
CBD primarily interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system. Our body naturally has millions of cannabinoid receptors throughout the body (Organs, Skin, and our Digestive Tract) and the phytocannabinoid CBD helps with the four primary functions of the endocannabinoid system: neuroprotection, stress relief, immune response, and regulation of the body’s general state of balance (appetite, sleep, mood, pain, etc.).
What Exactly Is THC and How Does It Work?
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), is a naturally occurring, psychoactive ingredient found in Marijuana used in conjunction with CBD to be used for various treatments through the endocannabinoid system.
THC has adverse effects to the biological structures of the brain via the endocannabinoid system, but also has positive effects for certain ailments or symptoms: anti-nausea effects, increased appetite, altered thinking (both a positive and negative), euphoria, and pain relief. The primarily affected areas of the body for these positive effects (in order with the list above) are: Brain Stem, Hypothalamus, Neocortex, Nucleus Accumbens, and the Spinal Cord.

What Is The Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system refers to a collection of cell receptors and corresponding molecules. You can think of cell receptors like little locks on the surface of your cells, and the keys to these locks are called endocannabinoids. Each time an endocannabinoid binds to a cell it relays a message, giving your cell-specific direction. There are two different types of cannabinoid receptors: CB1 and CB2.
CB1 receptors are found primarily in the brain and responsible for the psychoactive effects of marijuana. CB2 receptors are mainly expressed in immune tissues highlighting the immunomodulatory role of the endocannabinoid system (inflammatory conditions and the immune system). Each time an endocannabinoid binds to a cell, it relays a message, giving your cell specific direction, making CBD / THC a catalyst for increased or decreased function of certain tasks assigned to the endocannabinoid system.
With all this information, how can we know what we are buying online or in our local smoke shops (in reference to CBD) is potent enough to assist with the symptoms we are trying to alleviate?
For this question you need to examine the product you intend on using, and research it’s bioavailability along with percentages of inactive ingredients to carry the CBD. This will allow you to see the effectiveness of the cannabinoid in question entering into your bloodstream and activating the appropriate channels of the endocannabinoid system.

Confused Yet?
I know we have covered a lot of information, but we are now getting to the good part! Then you can show this article to all your friends, proving you know more about cannabis than they will every know… unless they read the article.
Dosing!
This is for interested physicians and consumers alike, since CBD is not regulated.
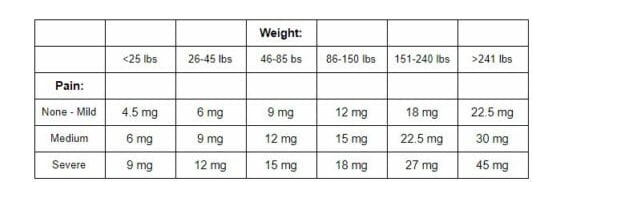
Simply adjust the MG amount (usually 1–6 MG per 10 lbs) to the severity of the symptoms! Cannabinoids, particularly CBD, demonstrate a bell-shaped dose-response curve; therefore, it is imperative that you slowly up the optimal dose without going over. To find an optimal dose, you should eliminate the use of any cannabis product for two days. Most prefer to start using CBD about two hours before bedtimes, starting with 10–15mg of active cannabinoids once daily, increasing the dose slowly every 2–3 days to determine if a better therapeutic effect results.
Try to find CBD supplements that are derived from Hemp Extract. Hemp Extract is a non-psychoactive substance found in cannabis plants. This extract contains high amounts of CBD, used for boosting the endocannabinoid system for your benefit. It is legal in all 50 states, so if you are one of the unlucky ones outside a progressive medical cannabis state, you can still find Hemp Extract CBD products at your local pharmacy, smoke shop, doctor’s office, or e-commerce store.
Zen Nutrients is dedicated to providing the highest quality supplements that can be found on the planet. By combining industry knowledge with simplistic ingredients, their products speak for themselves and stand alone in the continuing epic of natural and healthy treatment.
These supplements are GMO-Free, Gluten-Free, expertly designed in a certified cGMP facility, and crafted in the USA.

Written by Zen Project Manager, Matthew Banther
